1. Building Block View
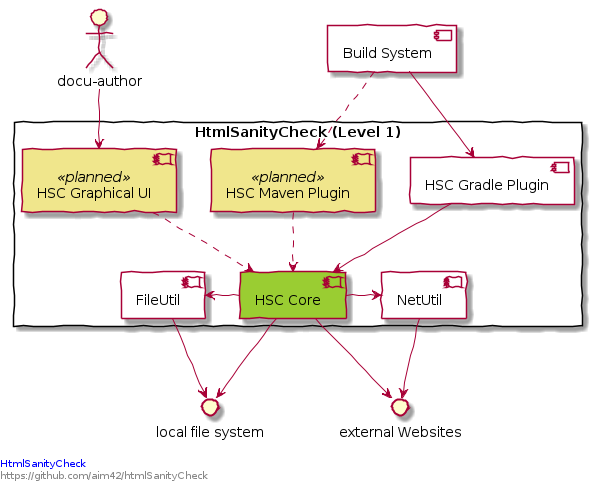
1.1. Whitebox HtmlSanityChecker

- Rationale
-
We used functional decomposition to separate responsibilities:
-
CheckerCore shall encapsulate checking logic and Html parsing/processing.
-
all kinds of outputs (console, html-file, graphical) shall be handled in a separate component (
Reporter) -
Implementation of Gradle specific stuff shall be encapsulated.
-
- Contained Blackboxes
hsc core: html parsing and sanity checking, configuration, reporting. |
|
HSC Gradle Plugin |
integrates the Gradle build tool with HtmlSC, enabling arbitrary gradle builds to use HtmlSC functionality. |
HSC Maven Plugin |
(planned, not yet implemented) |
HSC Graphical Interface |
(planned, not implemented) |
- Interfaces
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
usage via shell |
arc42 user uses a command line shell to call the HtmlSC |
build system |
currently restricted to Gradle: The build system uses HtmlSC as configured in the buildscript. |
local-file system |
HtmlSC needs access to several local files, especially the html page to be checked and to the corresponding image directories. |
external websites |
to check external links, HtmlSC needs to access external sites via http HEAD or GET requests. |
1.1.1. HSC Core (Blackbox)
- Intent/Responsibility
-
HSC_Core contains the core functions to perform the various sanity checks. It parses the html file into a DOM-like in-memory representation, which is then used to perform the actual checks.
- Interfaces
| Interface (From-To) | Description |
|---|---|
Command Line Interface → Checker |
Uses the #AllChecksRunner class. |
Gradle Plugin → Checker |
Exposes HtmlSC via a standard Gradle plugin, as described in the Gradle user guide. |
- Files
-
-
org.aim42.htmlsanitycheck.AllChecksRunner
-
org.aim42.htmlsanitycheck.HtmlSanityCheckGradlePlugin
-
1.2. Building Blocks - Level 2
1.2.1. HSC-Core (Whitebox)
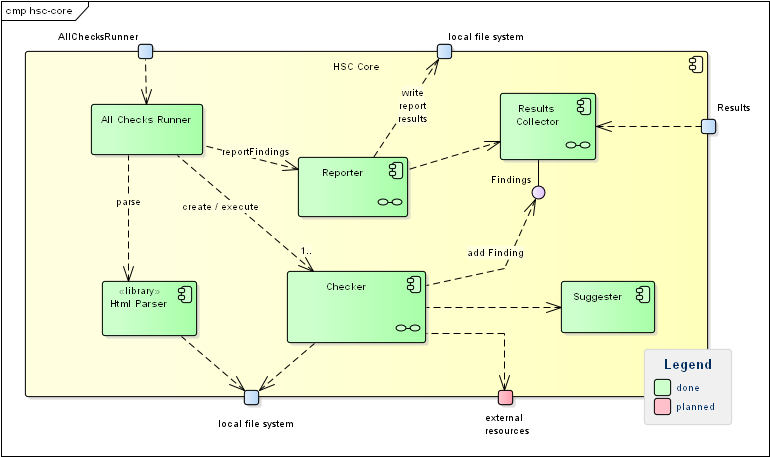
- Rationale
-
This structures follows a strictly functional decomposition:
-
parsing and handling html input
-
checking
-
collecting checking results
-
- Contained Blackboxes
Checker |
Abstract class, used in form of the template-pattern. Shall be subclassed for all checking algorithms. |
AllChecksRunner |
Facade to the different Checker instances. Provides a (parameter-driven) command-line interface. |
Collects all checking results. Its interface |
|
Reporter |
Reports checking results to either console or an html file. |
HtmlParser |
Encapsulates html parsing, provides methods to search within the (parsed) html. |
Suggester |
In case of checking issues, suggests alternatives by comparing the faulty element to the one present in the html file. Currently not implemented |
1.2.2. Checker and xyzChecker Subclasses
The abstract Checker provides a uniform interface (public void check())
to different checking algorithms. It is based upon the concept of extensible checking algorithms.
1.3. Building Blocks - Level 3
1.3.1. ResultsCollector (Whitebox)
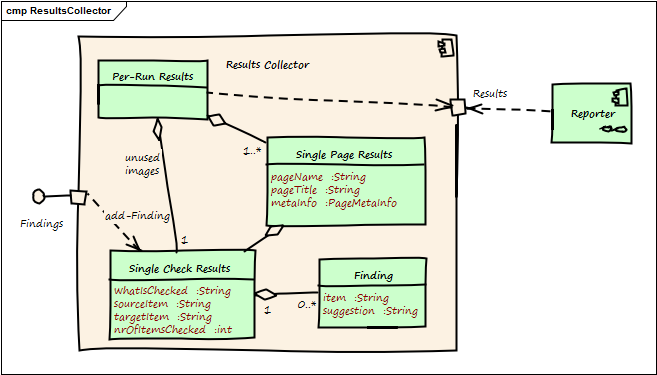
- Rationale
-
This structures follows the hierarchy of checks - namely managing results for:
-
a number of pages/documents, containing:
-
a single page, each containing many
-
single checks within a page
-
- Contained Blackboxes
Per-Run Results |
results for potentially many Html pages/documents. |
Single-Page-Results |
results for a single page |
Single-Check-Results |
results for a single type of check (e.g. missing-images check) |
Finding |
a single finding, (e.g. "image 'logo.png' missing"). Can hold suggestions and (planned for future releases) the responsible html element. |
Interface Results
The Result interface is used by all clients
(especially Reporter subclasses, graphical and command-line
clients) to access checking results. It consists of three distinct APIs for
overall RunResults, single-page results (PageResults) and single-check results
(CheckResults). See the interface definitions below - taken from the Groovy-
source code:
public interface RunResults {
// returns results for all pages which have been checked
public ArrayList<SinglePageResults> getResultsForAllPages()
// how many pages were checked in this run?
public int nrOfPagesChecked()
// how many checks were performed in all?
public int nrOfChecksPerformedOnAllPages()
// how many findings (errors and issues) were found in all?
public int nrOfFindingsOnAllPages()
// how long took checking (in milliseconds)?
public Long checkingTookHowManyMillis()
}public interface PageResults {
// what's the title of this page?
public String getPageTitle()
// what's the filename and path?
public String getPageFileName()
public String getPageFilePath()
// how many items have been checked?
public int nrOfItemsCheckedOnPage()
// how many problems were found on this page?
public int nrOfFindingsOnPage()
// how many different checks have run on this page?
public int howManyCheckersHaveRun()
}public interface CheckResults {
// return a description of what is checked
// (e.g. "Missing Images Checker" or "Broken Cross-References Checker"
public String description()
// returns all findings/problems found during this check
public ArrayList<Finding> getFindings()
}Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.